Docker Introduction
Lets say we have a Java based reservation application which depends on JRE, MySQL and Tomcat to run. To have this application setup we need to install all these dependencies, configure and then run the application. Not just on single environment, we need to do this setup in multiple environments like in development, testing and production. This setup and configuration process needs a lot of maintenance and also time consuming.
Docker provides an alternative way to setup applications using containers. Instead of installing application on the operating system we can install them on the docker containers. We can install multiple applications in a container. Container is a runtime instance on which we can run multiple applications. Each container runs on a separate process. We can have multiple containers running at same time and docker will manages these containers.
For example, you can assume container as something like JRE. JRE provides a runtime layer on top of operating system and java applications with out the knowledge of underlying operating system and hardware runs on this JRE. Likewise, container is a linux kernel which can be executed on any operating system and we can run any docker supported application on top it and these applications gets an illusion as they are running on there own machine.
Below image is from docker website which gives the idea of how docker works;
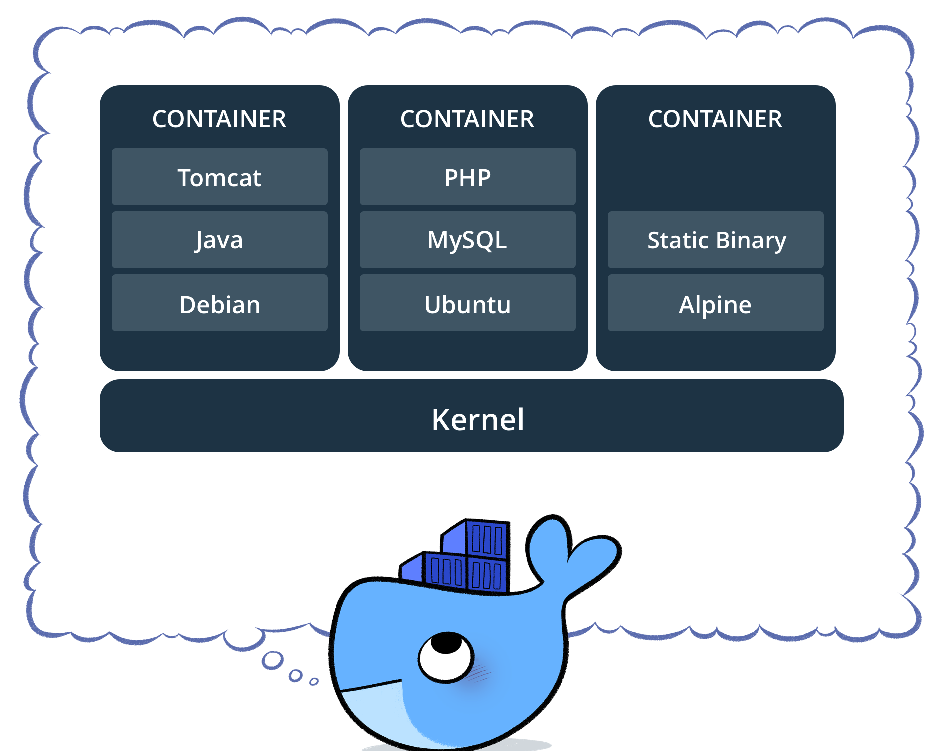
Docker Terminology
Les go through three main concepts in the docker;
Docker Image
How to create containers? we can create containers using image file and containers are instances of this image file. Docker image acts something like a java source file. Image file contains a set of commands which docker can understand and when we run this file, docker will execute these command and creates a container instance.
We may no need to write image files for most of the basic requirements because already there are many image files hosted on Docker Hub. Docker hub acts like a maven repository in java world but instead of repositories it will have docker image files. It is recommended to have a docker hub account so we can browse, download or create one.
Docker Engine/daemon
Docker engine/daemon is a background process which creates, runs and manages containers. We use docker CLI to interact with the engine.
Docker CLI
Docker provides a CLI interface. We can interact with the engine by passing commands through the CLI. CLI passes our commands back to the engine and displays output from the engine. CLI uses REST API to connect the engine and this network layer make engine and CLI work independently, because CLI and engine communicate based on the REST so CLI can also pass commands to the remote docker engine.
Installation
Docker comes with two editions; Community and Enterprise editions. Community is free for development and enterprise is a priced version which comes with a support. Installing docker is a simple process. Go through docker download page to download and install. Once the installation is complete then open the terminal and execute below command to check docker version;
$ docker --versionConclusion
We can get a fully configured application in a container when we run a docker image. We can run this image on multiple environments or run multiple images in same machine. Docker makes its easy to setup and configure applications.
