Spring Cloud Gateway - Part 1
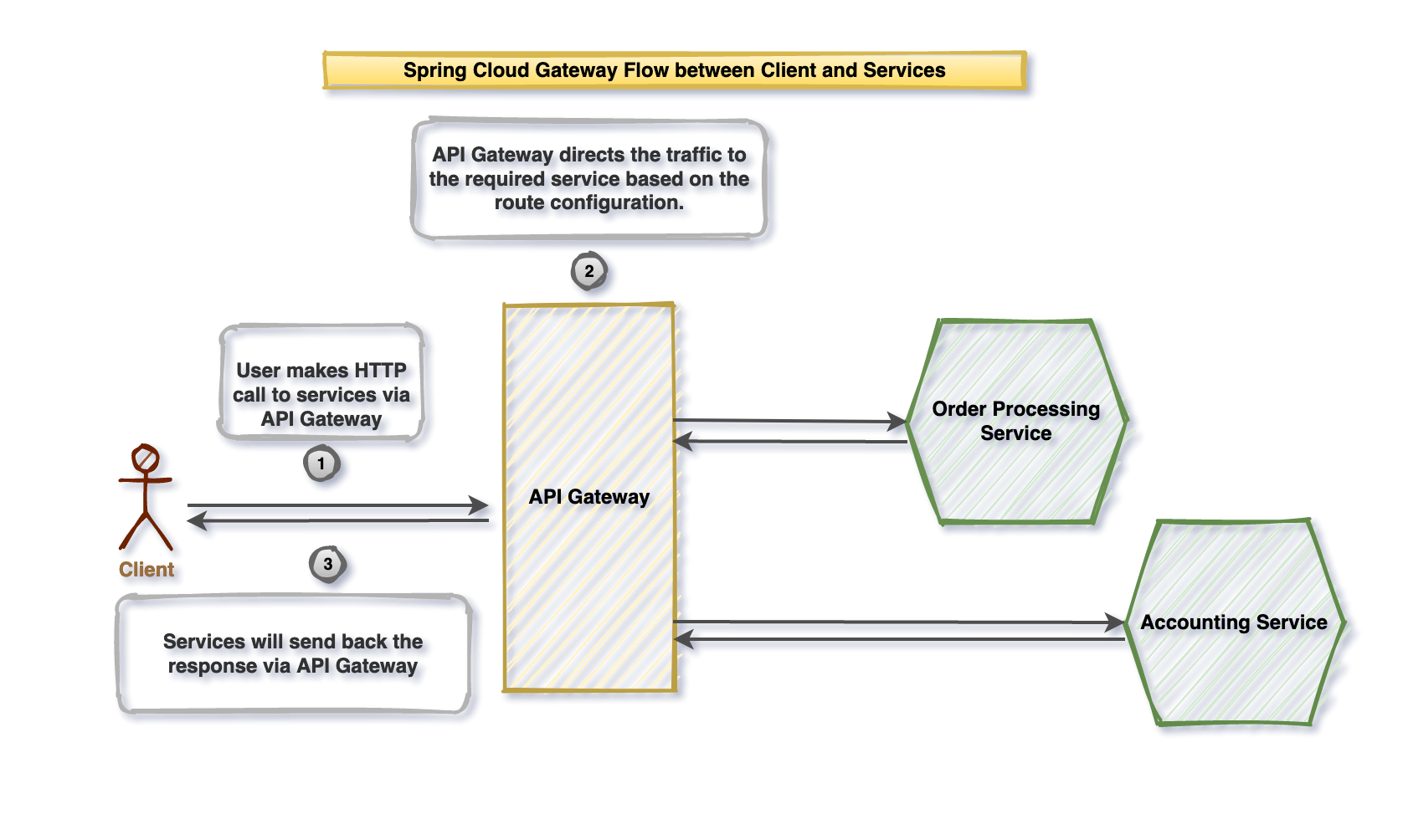
API Gateway is the entry point to the application, through which the client (Web/Mobile/Desktop) can make REST API calls. API Gateway will allow us to secure the endpoints, throttle, and monitor the traffic.
Many open-source libraries are available for creating an API Gateway, like Netflix Zuul and Amazon API Gateway. In this article, we will look at creating a project using Spring Cloud Gateway.
Spring cloud gateway simplifies the creation of API Gateway service. We should have a separate API gateway service in the production environment without any business logic; this will allow us to deploy or change the API gateway without impacting other services.
We only need to make changes in the application.yml file to configure the routes, and we can create a Spring cloud gateway project by simply going to start.spring.io and selecting gateway dependency.
You can click this link to see my preconfigured spring cloud gateway project. Download and import into your editor.
We need to understand three concepts to work on the Spring cloud gateway project.
- Route: Route is the combination of destination URL, predicate, and filter.
- Predicate: These are like ‘if’ conditions. If the predicate is true, then the request is directed to the configured Route.
- Filter: To modify the request and responses.
I used HttpBin to configure gateway endpoints. Httpbin is the free HTTP request and response service.
Configure Routes
Open application.yml and modify it with the below content;
server:
port: 9091
spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: one
uri: https://httpbin.org/
predicates:
- Path=/get- API gateway will listen on port 9091.
- Configure routes under ‘spring.cloud.gateway.routes’ property. In this file, we configured one Route.
- Route will have a unique id, destination URL, and a list of predicates or filters. In this case, we have one predicate.
- Spring cloud gateway provides many predicates. For example, some of them are Path, Header, Cookie, and Query. In our example, we used the Path predicate. Predicates are recognized by the predicate type (Path, Cookie, Header), followed by an equal sign (=), followed by argument values separated by commas (,).
Run the application and execute a CURL command to make a get request on ‘http://localhost:9091/get.’
curl http://localhost:9091/get
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Content-Length": "0",
"Forwarded": "proto=http;host=\"localhost:9091\";for=\"0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1:56684\"",
"Host": "httpbin.org",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.54.0",
"X-Amzn-Trace-Id": "Root=1-5fbbe24c-076ada6d328a832d22e38d51",
"X-Forwarded-Host": "localhost:9091"
},
"origin": "0:0:0:0:0:0:0:1, XX.XX.X.XXX",
"url": "https://localhost:9091/get"
}We made a GET request on /get endpoint, and this request will match with the Path ‘/get’ which we mentioned in the Predicate, so the request directs to https://httpbin.org/.
In the next section, we will see an example of Header Predicate.
Header Predicate
Matches with a header in the HTTP request. To make it simple, I am showing only the predicates section instead of the whole configuration file.
predicates:
- Header=App-Context-Id,^[a-zA-Z0-9]+$Matches only if the request contains a header ‘App-Context-Id’ with any alphanumeric value.
Go through this link to see all available Predicate’s in Spring Cloud Gateway
Conclusion
We went through the basics of Sping API gateway components and worked on a sample project to configure a route using Path and Header predicates.
